Depression ICD-9 296.3
Lecture Video and Power Point Notes for
The Inflammation-Depression Connection
Melbourne, Australia, August 19, 2012 at
The 6th Annual A5M Conference In Anti-Aging & Aesthetic Medicine
News
You may have seen all the media on ABC, CBS, NBC, CNN, FOX, The Today Show, and many others about how Wiggle front man, Anthony Field, one of many celebrities with depression, that was handicapped by chronic pain, chronic fatigue, misdiagnosed fibromyalgia and clinical depression during his 20 years on the road.
Watch Anthony Field’s interviews on CNN and The Today Show where he discusses the inflammation-depression connection approach;
CNN Shanon Cook Interviews Anthony Field, a celebrity with depression who had what he called a mental breakdown but not a nervous breakdown. He healed himself by disconnecting the Inflammation-Depression Connection, one of the theories of depression Dr Stoxen mentions in this article and presentation. click here
THE TODAY SHOW! Anthony Field Shares How an All Natural Approach and Surviving Depression, click here
 Depression represents a major public health problem. In Australia, Major depression accounts for more days lost to illness than almost any other physical or mental disorder. Approximately 20% of people will be affected by depression and 6% will experience a major depressive illness. Studies have also shown that there is a correlation between chronic depression and the development of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and dementia later in life.
Depression represents a major public health problem. In Australia, Major depression accounts for more days lost to illness than almost any other physical or mental disorder. Approximately 20% of people will be affected by depression and 6% will experience a major depressive illness. Studies have also shown that there is a correlation between chronic depression and the development of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and dementia later in life.
There is substantial literature linking inflammation with the risk for depression. The purpose of this presentation is to list the inflammatory mediators and their link to depression and inflammatory disorders such as MS, cardiovascular disorders, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Increase inflammatory cytokine expression and the development of concurrent psychiatric symptoms were initially observed after administration of cytokine therapy to patients afflicted with cancer hepatitis and MS. It has been found that patients with depression have high levels of inflammatory biomarkers. This suggests that inflammation can be a mediator for depression.
In this lecture presentation I review these studies and determine their potential to lead to interventions which may reduce the risks for inflammatory diseases of aging such as osteoarthritis cardiovascular disease and the symptoms related to varying degrees of depression.
Watch Below as Dr. Stoxen gives his lecture presentation ‘The Inflammation-Depression Connection, Melbourne, Australia, August 19, 2012 at 6th Annual A5M Conference In Anti-Aging & Aesthetic Medicine
Dr Stoxen reviewed over 2000 of the latest scientific papers extensively before he did this presentation.
I work in the sports and entertainment industry and at times ‘my back is against the wall’. An example might be an entertainment group comes in for a weekend and i’m asked to solve a major chronic or clinical arthritic problem in less than 48 hours.
What your talking about is doing is exceeding the standard of care. It’s like compressing 60 office visits in a period of 24 to 48 hours. The treatment can be quite aggressive and life changing for the patient.
Let’s say for instance you have a boxer that has a neck injury and that boxer is put in the ring only a week before the competition and there is 25 to 30 million dollars involved in the competition. There are hundreds of people involved in this event.
Three days a week of nero muscular re education and back adjustment just doesn’t cut it anymore.
What I have learned is that the current standard of care in my opinion doesn’t really meet what is required to actually make a difference in the levels of inflammation i’m seeing. Yet in the United States the insurance company reimburses us 20 minutes office visits. This only scratches the surface as far as reducing some of that inflammation that is causing the depression and then they may end up being chronic.
I hope I can open your eyes to some new concepts that may help you in connecting the Inflammation-Depression Connection
Below is the lecture and power point notes used for Dr. Stoxen’s lecture to assist you in connecting The Inflammation-Depression Connection Approach:
Depression
- Increasing 10% every decade since 1910.
- The leading cause of disability in the United States.
- The number of Americans taking antidepressant drugs doubled in the decade from 1996 to 2005, from 13.3 million to 27 million.
- Today 10% of every man, woman and child in America takes an antidepressant or some drug.

“Depression is becoming a very serious problem in the United States as well as in Australia. The number of Americans taking anti-depressants in the United States is actually up to 30 million!”
“I am not sure if you aware but there was a recent shooting in Aurora, Colorado. The concern was the medication that was given to this young man, who was actually very bright. He decided to shoot and kill other people. The medications i’m talking about on the label state that it may cause someone to have thoughts of suicide or a desire to kill others.”
“Certainly with 30 million people taking anti-depressant medication it adds up to be a potential of 900 thousand people who are interested in killing somebody. Weather that be themselves or someone else. If we have that information and see that as a potential problem, as a physician we might want to think about other possible treatments for the patient besides these medications.”
“I am not saying to take patients off medication and certainly I don’t do that. What I do is treatment that will enhance the medication or treatment that is provided and if the doctor and I are working together we can see if we can help the patient wean off the medication.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
DSM Criterion for Major Depression
- A period of at least two weeks during which there is either a depressed mood or the loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities.
- In children and adolescents, the mood may be irritable rather than sad.
- The individual must also experience at least four additional symptoms drawn from a list that includes changes in appetite or weight, sleep, psycho motor activity, decreased energy, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty thinking, concentrating or making decisions, or recurring thoughts of death or suicide, plans or attempts.
- The episode must be accompanied by clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or important areas of functioning.
- It’s normal for people to feel a range of moods.
- It’s not realistic for people to be in a great mood all the time.

“I don’t know if you have kids but I have a 17 year old and she is irritable at times.”
“What we have to understand is that at the time the patient does come to us they may be depressed and next week they may not be depressed. People are allowed to have different moods. Sometimes people might say, “It’s just not my day.”
“Instead of just putting the patient on an anti-depressant we might want to consider the patients lifestyle changes such as getting more exercise or fresh air.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, 1994 (DSM-IV).
Office Visit for Major Depression?
The doctor reviews tests conducted by the nurse and then spends less than 10 minutes with the patient.

“Is this your typical doctors visit?”
“Here’s something to help your cholesterol, something for your blood pressure, and for your depression, here is an antidepressant. You shouldn’t have too many side effects ,though you might experience a loss of sex drive, but we have another drug for that. Would you like me to add that to your prescriptions? Good luck and I’ll see you in three months when your prescriptions run out.”
“Certainly that is not how most of the people in this room practice nor do I but this is the reality we are dealing with in some doctors offices, today.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
The administration of high concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines often leads to a condition known as systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)

“Cytokine-Induced Syndrome commonly mimics depressive like symptoms. It’s almost like having a cold all the time.”
“One of my patients was talking to me about his chronic pain and he said, ‘It feels like I have a cold all of the time, I can’t get out of bed, I can’t sleep at night, I really don’t want to talk to people this was sickness syndrome.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Inflammation and Depression Painful and Silent Arthritic Inflammation
- After reviewing over 1,000 citations linking inflammation to depression we can make the assumption that inflammation is linked to and perhaps a leading cause of depression.
- When our bodies release inflammation that leads to chronic pain, worry or have stress our bodies release low-grade inflammation.
- When we have chronically high levels of inflammation, feel chronic pain, worry or have stress our bodies release comforting levels of serotonin to help us cope.
- The body feels as if it is being attacked. We also have depression when we are unable to meet the demands or challenges of these attacks, leading to more stress.
- Patients consciously and subconsciously feel hopelessly locked up by three conditions, inflammation, chronic pain and depression.
Unemployment
Finnish scientists found that stress-induced low-grade inflammation might be a link between unemployment and ill health.
Coronary Artery Disease
In a study of over 677 participants, 433 had no depressive symptoms, 86 had depressive symptoms at one assessment, and 138 had depressive symptoms at two or more annual assessments. Across all three groups, greater depressive symptoms were associated with higher subsequent levels of IL-6.

“This could be the fact that, ‘gee I have coronary artery disease’ so i’m not so happy.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Pollution
In experiments, mice subjected to the same particulate matter as that of a major city displayed more depressive-like responses and impairments in spatial learning and memory as compared with mice exposed to fresh air.
Cigarette Smoking
Lifelong cigarette smokers have a higher prevalence of common diseases such as atherosclerosis and COPD with significant systemic impact.
A low-grade systemic inflammatory response is evident in smokers as confirmed by numerous population-based studies. Some inflammatory mediators are still significantly raised in ex-smokers up to 10 to 20 years after quitting, suggesting ongoing low-grade inflammatory response persisting in former smokers.
Yanbaeva DG, Dentener MA et al. Systemic effects of smoking. Chest. 2007;131(5):1557-1566.
Gut Inflammation Vagus Nerve – Blood-Brain Barrier
- Peripheral pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and IL-6 can affect central nervous system functioning by penetrating the blood-brain barrier directly through active transport mechanisms.
- Inflammation can move from the periphery to the brain directly through activation of the afferent through the Vagus nerve.
- A group of studies have shown that the primary cause of inflammation may be a dysfunction of the gut-brains axis. This is a bidirectional mechanism.

“Here is a question I have been asking a lot of the doctors here. How to peripheral cytokines enter the brain? I can’t get a good answer. This is perplexing. This is not my speciality but I would like to know why people who have peripheral cytokines such as high levels of IL-6 have depressive syndromes. Why do the administration of these drugs actually cause the brain to react with depression?”
“I’m still looking for the answer to this question. There are some hypothesis but no definitive answers.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Memory
Low performances in immediate verbal recall and delayed verbal recall are associated with higher IL-6 levels in women with recurring major depressive disorder.
The results of this study it suggests the existence of an association between inflammatory imbalance and cognitive impairment in major depressive disorder.

“Brain fog and memory loss were also found with people suffering with depression.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Suicide
The results of studies demonstrate for the first time that suicidal patients display a distinct peripheral blood cytokine profile compared to non-suicidal depressed patients. This study provides further support for a role of inflammation in the patho physiology of suicide.
Post-Stroke Depression
The cause of post-stroke depression is still not clear. However, studies have indicated that immune dysregulation plays a role in the patho physiology of depression. What was found was a significant increase in the cytokines:
- IL-6, IL 10
- TNFa
- Interferon Y
- The ratios of IL-6/IL10 TNFa/IL10 were also elevated.
Overweight and Obesity
- Depression (and the inactivity plus diet changes associated with it) cause obesity.
- The obesity leads to inflammation, which cycles back around to lead to depression.
- Depression may lead to inactivity and dietary changes, which leads to obesity, which leads to inflammation.
- Obesity associated inflammation that affects the brain may promote addictive behaviors, leading to a self-perpetuating cycle that may affect not only foods but addictions to drugs, alcohol and gambling.
- Targeted diet and exercise programs are beneficial

“The patient I was speaking about earlier had an addictive behavior it was called a gambling problem. An addiction to drugs as stated above could very well be an addiction to the pain killers that the patient is taking to ease the pain from the inflammation.”
“In the United States more people die from prescription drug overdose than in car accidents. In 2004 more people died from prescription drugs (more likely pain killers) than all the street drugs such as heroine and cocaine combined.”
“What is sad is we see celebrities and others dying of misuse of these prescription drugs and the next week we completely forget about it.”
“Something must be done to decrease the use of these prescription drugs. They can cause illness, side affects and death.”
“There are other alternative methods we can try.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Inflammation and the IDO Pathway
- Idoleamine 2.3-dioxygenase IDO + tryptophan 2.3-dioxygenase (enzyme) competes with tryptophan metabolism which reduces serotonin.
- Tryptophan is metabolized to kynurine by kynurine hydrxygenase to kynurine acid (KYNA) which antagonizes A7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, which leads to striatal dopamine release, which is in the brain of depressed patients.
- Kynurine is converted with enzyme kynurine 3-monoxygenase (KMO) to quinolinic acid (QUIN).
- QUIN activates N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptors and releases glutamate.
- This leads to the formation of neurotoxins such as the glutamate agonist quinolinic acid and contributes to the increase in apoptosis of astrocytes, oligodendroglia and neurons.
- QUIN, kynurine and glutamate are all implicated in pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, ALS and dementia.

“The way the serotonin uptake inhibitors work is they inhibit the re uptake of serotonin however if the inflammation is actually the cause of decrease in the tryptophan that trips all of these chemical reactions that are linked to plaquing and these other diseases of aging then why are we concentrating on that?”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC

“We know that Inflammation is one of the major triggers in depression as well as in these other diseases of aging. We must be more aggressive in treating the cause of the inflammation!”
“Anti-aging medicine is to find and prevent the earliest detection and prevention of age related diseases.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- In mild to moderate depression, the benefit may be mild to zero.
- In severe depression the improvements may be more substantial.
- Sometimes the drug takes 6-8 weeks to work.
- In studies, there are sexual side effects in approximately 17% to 41% (likely to be overestimated when there are no placebos).
- There is a decrease in dopamine and norepinephrine which could lead to erectile dysfunction.
- However, the sexual side effects may be the same with another drug.
- There is dependence withdrawal, which may be severe.

“How do we know that the patient isn’t just having a bad month and then the next month it might be better?”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
- Hu XH et al. Incidence and duration of side effects and those rated as bothersome with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment for depression: patient report versus physician estimate. Journ Clin Psy. 2004;65(7):959-65.
- Landén M et al. Incidence of sexual side effects in refractory depression during treatment with citalopram or paroxetine. Journ Clin Psy. 2005;66(1):100-6.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- At first people feel wonderful.
- They feel as if the cloud lifted.
- They feel they can handle minor issues more easily.
- They are hopeful, confident and feel improved self-worth.
- These drugs are not addictive but patients do feel dependent.
- When they want to wean themselves off the drug without healing the body of inflammation and other causes, they experience withdrawals which are severe.
- Patients expect you to put them on antidepressant drugs.
- When you suggest options to these drugs patients are relieved they have these options.
- If you do have to put patients on antidepressants, it is not a sign of failure, but never give up trying to help the patient be self-sufficient.
- This is best for everyone.

“I have patients that are scared to get off these medications because they are so used to taking them. They expect you to put them on anti-depressant medications. But if you have an alternative they might be willing to try.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Selective Serotonin Uptake Inhibitors
Neuropsychopharmacology 2011
- A study of 22 studies data showed that overall while pharmacological antidepressant treatments reduced overall depressive symptoms it did not reduce levels of TNFa.
- However antidepressant treatment did reduce levels of Il-1b and possibly IL-6.
- While efficacious for depressive symptoms, did not appear to reduce cytokine levels

“Even though the antidepressant medication may reduce the overall symptoms, the inflammation is still ongoing. Studies have shown that inflammation is linked to cardiovascular problems, depression, neurologic diseases of aging and other diseases.”
“We must treat the inflammation!”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
What Happens if You Take a Drug to Lower Serotonin?
There is a drug that lowers serotonin and it has the same effectiveness as the drugs that increase available serotonin. It has been shown to be as effective as some selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
So how can it be that one drug lowers it and one drug raises it and they both have the same effect on depression?
Most serotonin reuptake inhibitors are not as effective as you think.
- JAMA 2002 article about a study in the NIH stated a particular popular SSRI had about the same or a little better results than placebo.
- JAMA 2010 January 6, 2010 stated the real biochemical effect of SSRIs as nonexistent to negligible for severe depression.

“I don’t prescribe serotonin reuptake inhibitors. I’m forced to do whatever I can alternatively to help the patient.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
- Walsh BT, Seidman SN, Sysko R, Gould M. Placebo response in studies of major depression: variable, substantial, and growing. JAMA. 2002;287:1840-1847.
- Fournier JC, DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD et al. Antidepressant Drug Effects and Depression Severity: A Patient-Level Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2010;303(1):47-53.
Where to Attack Depression More Aggressively
In inflammatory pathways creating pro-inflammatory cytokines, specifically IL-1, IL-6 and TNFa.
Ways to Disconnect The Inflammation Depression Connection
- Moderating cytokines which start the process
- Inhibition of this pathway with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- Addressing targets in the kynurenine pathway

“One of the most novel approaches I feel, is to moderate the cytokines which start the process”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Inflammation Approach to Treating Depression
- Treat Inflammatory Diseases- Like Hepatitis, Heart Disease
- Reduce Pulmonary Inflammation
- Inflammation of the Skin-Psoriasis – 60% have depression in their life
- Dietary Inflammation
- Arthritic Inflammation
Where I Attack Depression – Inflammation
If you prescribe a cholesterol-reducing drug – you talk about diet.
If you prescribe an antidepressant, do you talk about inflammation?
Levels of Inflammation

” This is a chart I developed 20 years ago. The red represents painful inflammation. The yellow represents silent inflammation. The green represents normal inflammation. The gold would represent somewhat of an Olympic Athlete.”“What i’m focusing on is silent inflammation. The patient might say they don’t have pain there but I know they do because I see the pattern of your walk and I know the patient will have pain in a certain area. I might put pressure on that area and the patient does feel it.”
“It’s like getting a massage and they find those knots that you didn’t know you had. That is called silent inflammation. It might not be painful to the brain but it’s damaging to the body.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
- It is low-grade inflammation.
- Low-grade inflammation is what research is telling us contributes to depression.
- Painful Arthritic Inflammation
- Silent Arthritic Inflammation
We know how to find painful arthritic inflammation.
- How do we examine for silent arthritic inflammation?
- How do we treat silent arthritic inflammation?

“Connect the knots. In other words the knots are connected throughout the body in a way that forms a pattern that is determined by the pattern of your walk or gait.”
“So if you walk for me I can determine where you may have pain in your body.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC

“There is no way if you have a patient that has an abnormal movement pattern of banging and twisting for 10 – 20 years and then for 20 min a day at three days a week your going to reverse the affects of that? I don’t think so.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Vibration Therapy
Vibrational Massage from the feet to the head
- 45 minutes before treatment
- Stimulates circulation to flush the inflammatory chemicals out of the body
- Increases the levels of Oxygen, nutrients and hormones

“This is a tremendous therapy for patients and you can do the same in your office.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC

“Some people ask me how come I have some many celebrity and VIP patients? Certainly it’s not the location of my office as it’s in a very tough area in Chicago, IL USA. The reason why is because of the results.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Exercise is a Powerful And Safe Antidepressant
Depression and exercise: A 1999 study by researchers at Duke University, published in the Archives of Internal Medicine, compared exercise, medication, and a combination of the two among a group of 156 middle-aged and elderly patients with non-suicidal depression. Medication was a selective serotonin re uptake inhibitor.
- The exercises were performed three times a week for 45 minutes and included 30 minutes of brisk walking or jogging.
- After 16 weeks all three groups showed similar improvements.
A follow a to this study published in psychosomatic medicine in 2000 check back on how the patients were doing six months after the study.
- The exercise-only group was actually doing better than the other two.
- Fewer than one third of the medication-free exercisers had relapsed back into depression, compared to over half of the patients in the med and the med/exercise groups.

“After we release the spring mechanism and allow the cytokynes to decrease and the muscle spasms are out of the kinematic chain, then we recommend exercise.”
“It’s nice to know that it was the exercise that actually helped with the depression. This causes the patient to go back and exercise.”
“Exercise must be performed in movement patterns that won’t increase the levels of inflammation. Be sure the spring mechanism is not locked. Releasing the spring mechanism will allow the body to bounce back from the impacts from even simple walking.”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
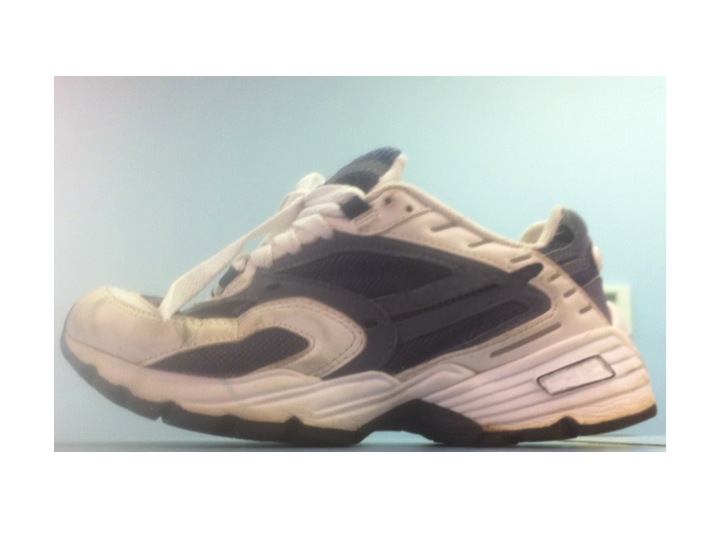
Take a look at the footwear

“Notice this shoe.
The toe is turned up in the front as well as a split sole.
I would not recommend this shoe.”
I would advise the patient to get a shoe with an extended medial counter support that keeps the foot in the safe range.” (see the illustration below)
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Diet, Supplements, Exercise, and an Aggressive Attack on Inflammation
Diet can have a profound affect on inflammation and therefore depression.
Discuss how food is the patient’s new drug.
What they eat could be a drug that increases or decreases depression.
Fat
Decreased cholesterol below 160 can lead to depression
Omega 6 fatty acids – increase inflammation
- Vegetable Oils
- Corn Oils
- Egg Yolks
- Omega-3 fatty acids – decrease inflammation
Fish
Omega 3:Omega 6 used to be 1:1
Now 1:25 last 100 years
Omega 3 is for reduction of inflammation and nerve cell function
- Tanskanen A, Hibbeln JR, Tuomilehto J et al. Fish consumption and depressive symptoms in the general population in Finland. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(4):529-531.
- Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Belury MA, Andridge R et al. Omega-3 supplementation lowers inflammation and anxiety in medical students: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav Immun. 2011;25(8):1725-1734.
Omega 3
- Brain behavior Immunology 2010 – This study showed that 2.5 g of EPA–DHA mirrored the proportions of fatty acids in the typical American diet and that by supplementing patients with this amount there was a 14% decrease in IL-6 production and a 20% reduction in anxiety symptoms.
- Studies suggest that maternal DHA deficiency may lead to the development of major depressive disorder in pregnancy and postpartum. These studies are suggesting clinical benefit for supplementation with EPA in major depressive disorders.
- Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Belury MA, Andridge R et al. Omega-3 supplementation lowers inflammation and anxiety in medical students: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav Immun. 2011;25(8):1725-1734.
- Mozurkewich E, Chilimigras J, Klemens C et al. The mothers, Omega-3 and mental health study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2011;11:46.
L-Tryptophan and 5HTP and Cognitive Impairment
Older adults with mild cognitive impairment had significant improvements in several measures of cognitive function when supplemented with an oily immersion of DHA-phospholipids containing melatonin and tryptophan for 12 weeks.
Rondanelli M, Opizzi A, Faliva M, Mozzoni M et al. Effects of a diet integration with an oily emulsion of DHA-phospholipids containing melatonin and tryptophan in elderly patients suffering from mild cognitive impairment. Nutr Neurosci. 2012l15(2):46-54.
D/L Phenylalanine for Norepinephrine Deficiency
- D/L-Phenylalanine is converted to Tyrosine.
- Tyrosine is converted to Dopamine.
- D or L-Phenylalanine creates Dopamine and Norepinephrine.
- Tyrosine is the parent compound for Adrenaline.
- Norepinephrine- and Phenylalanin- like compounds exist in chocolate – That is why we crave chocolate when depressed.
- Some studies say D/L-Phenylalanine is as good as antidepressants.
- D/L-Phenylalanine – 500mg/day and up to 2-3000 mg/day.
Ruhé HG, Mason NS, Schene AH. Mood is indirectly related to serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine levels in humans: a meta-analysis of monoamine depletion studies. Mol Psychiatry. 2007 Apr;12(4):331-359.
Supplements That Support Mood
- B6 helps in production of serotonin from 5HTP
100 mg/day
- B12
100 mg/ day
500 mg/day with poor absorption
- 5HTP
- Antioxidants
- Mineral Supplements
CA+ 500 mg/day
Chromium 200-300 mg/day
- Fish Oil
Normal 1000 mg-5000 mg
Asthma, diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, cancer, injury, chronic pain – 5000 mg
Bipolar – 10,000 mg
Curcumin
Is a plant derived dietary spice with various biological activities including anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory effects. Its therapeutic applications have been studied in a variety of conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, colon cancer and depression.
Guimarães MR, Coimbra LS, de Aquino SG et al. Potent anti-inflammatory effects of systemically administered curcumin modulate periodontal disease in vivo. J Periodontal Res. 2011;46(2):269-279.

“Try to do everything you can to decrease the levels of inflammation.
Be more aggressive with the therapies. Take time with the patient.”
“Thank you very much for being such a great audience!”
–Dr. James Stoxen DC
Like this article? We will send the next one to you
Register for our updates below:
Disclaimer
All content on teamdoctorsblog.com, including without limitation text, graphics, images, advertisements, videos, and links (“Content”) are for informational purposes only. The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical treatment, advice, or diagnosis. Please remember to always seek the advice of a qualified physician or health professional with any questions you may have regarding any medical concerns. Dr James Stoxen DC and Team Doctors does not recommend or endorse any specific treatments, physicians, products, opinions, research, tests, or other information it mentions. Said Content is also not intended to be a substitute for professional legal or financial advice. Reliance on any information provided by Team Doctors is solely at your own risk.