I have been standing in these shoes all day! My Feet Hurt! Maybe the pain will go away…….
Those are six very dangerous words, maybe the pain will go away….
An activity as simple as standing all day can lead to pain in your feet. So you need to know how to protect your feet when you’re stuck standing for hours on end, especially on a hard surface.
Besides the stress of prolonged standing, the architecture of the foot can also increase the symptoms from pre-existing conditions: Plantar fasciitis refers to the inflammation of the fascia under the heel. Flat or tilted feet (from heel pronation) and bony spurs in the base of the ankle may make the condition worse. Achilles tendonitis results from over stretching of the Achilles tendon. Bunions at the side of the big toe may arise because of heel pronation and may be aggravated by narrow shoe boxes (the area in front of the shoe) and prolonged standing. Corns on top of the toes may be aggravated by scraping against the inside of your shoe.
WHAT ARE POSSIBLE HEALTH SYMPTOMS FROM STANDING ON YOUR FEET TOO LONG?
The most common symptom from prolonged standing on your feet, and usually the first to occur, is discomfort and fatigue in the legs.
The closer the body part is to the ground, the more likely it will be affected by prolonged standing (i.e. the feet are most often affected, followed by the shins and calves, followed by the knees, thighs, hips and low back). However, symptoms from working on your feet may reach to the top of your body. In some studies neck pain symptoms have been related to prolonged standing at work!
Beyond simple fatigue and discomfort, more serious health effects can result from working on your feet for long hours.
In lab experiments people could not distinguish fatigue in their legs from whole-body fatigue. Therefore, that whole-body fatigue feeling could be related to working on your feet.
Some of these are: Low Back Pain, Painful feet and other foot problems, Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Spurs, Orthopedic changes in the feet (e.g. flat feet), Restricted blood flow, Swelling in the feet and legs, Varicose veins, Increased chance of arthritis in the knees and hips
WHAT CAUSES THESE PROBLEMS?
Joint compression: Gravity squeezes your joints under the weight of your body. Each body part is compressed by all of the sections of the body above it. (For example, your hips are compressed by your head, arms and torso, but your feet are compressed by the weight of your whole body!)
Compressing a joint is like squeezing a sponge – body fluids are squeezed out of the space in the joint. Without body fluids and circulation, your joints become malnourished, and cannot continue to support the weight of your body. Wear and tear of body parts occurs.
Postural muscle fatigue: Postural muscles keep your body from falling over while you’re standing. Standing for a long time forces these muscles to work without a rest. Without rest these muscles become exhausted, resulting in pain.
These effects are like working without lunch. Joints and muscles get their “lunch” from circulation, and need rest breaks to recoup from bouts of work. Think how you would feel without lunch!
Insufficient venous blood return in the legs: Gravity pulls blood down into your feet. One way that blood is pushed back up to your heart is through cyclic muscle contractions, often called a “muscle pump“. If the muscles are engaged in one long contraction (sustained contraction) to keep you standing, they cannot produce a ‘muscle pump” effect. Continuous muscle contractions also hinder circulation of body fluids.
Keeping the body in an upright position requires considerable muscular effort that is particularly unhealthy even while standing motionless. It effectively reduces the blood supply to the loaded muscles. Insufficient blood flow accelerates the onset of fatigue and causes pain in the muscles of the legs, back and neck (these are the muscles used to maintain an upright position).
Standing too long not only produces muscular strain but other discomforts also. Prolonged and frequent standing, without some relief by walking, causes blood pooling in the legs and feet. When standing occurs continually over prolonged periods, it can result in inflammation of the veins. This inflammation may progress over time to chronic and painful varicose veins. Excessive standing also causes the joints in the spine, hips, knees and feet to become temporarily immobilized or locked. This immobility can later lead to rheumatic diseases due to degenerative damage to the tendons and ligaments (the structures that bind muscles to bones)
In my practice, I work 90 hours a week on average. What is worse is that I am standing on my feet the entire time.
How do I do that and still run barefoot?
If someone should have an excuse for why they can’t run or run barefoot it should be me.
This is my typical week:
I practice about 12 hours a day from 9:00am in the morning to 9:00pm at night, minimum five days a week. At least 3 nights a week I am working on my feet until midnight on a VIP client. I work at least one full day if not two on my feet on the weekends.
When you’re on your feet for an extended period of time, the muscles that suspend your feet or the spring suspension system muscles are in a sustained contraction that has to be maintained for a certain amount time.
What is sustained contraction and how does it lock your joints and specifically the human spring?
An example would be holding a glass of water in my hand. Although I can do this easily.
If I hold it for too long in a sustained contraction I am going to get tired. My arms will have an inflammatory reaction and be stiff. The stiffness can even lock up your joints.
What is foot lock?
The foot and ankle has 33 movable joints to allow the force of the landings to be spread out over these joints for a smoother landing.
When the foot locks in any one of the 33 joints this causes a less smooth landing and a compensation for the normal motion. Any abnormal motion in the foot will cause an abnormal motion in the entire flooring system of the 7 floors of human spring which eventually locks.
Do we see this clinically? Of course!
To think any different defies the laws of gravity, engineering and physics.
Can weakness in the suspension system muscles lead to a locked human spring?
- Standing on your feet all day leads to fatigue of the spring suspension system muscles which determines your ability to resist impacts of walking, recycle energy through the spring and provides for healthy movement.
- Stiffness in the spring suspension system muscles eventually leads to stiffness or locking of some of the 33 joints of the foot and ankle.
- When the human spring is locked at the foundation, the body compensates with abnormal motion through the entire seven floor human spring.
- Abnormal motion in moving parts leads to stress and strain of the muscles, ligaments and tendons that guide the movement of the bones and joints.
- Abnormal stress and strain leads to wear and tear of the joints.
- Wear and tear leads to the release of inflammation.
- The release of inflammation leads to pain, fatigue and accelerated aging of the musculoskeletal system and other systems of the body.
- High levels of inflammation (cytokines) have also been strongly linked to feelings of depression.
This is true when YOU stand too long.
The sustained contraction can lock the spring mechanism. The spring mechanism loses spring mobility and may not be as effective in springing our bodies off the ground upon impact from the forces of the landings.
We were designed to function optimally if we keep moving so that the spring suspension doesn’t settle, drop and lock.
The theory states that once your foot and kinematic spring chain lock then the body bangs into the ground instead of springing off the ground. The landing becomes a bang and twist instead of a spring and roll. (see below)
When you stand too long your muscles have a sustained contraction similar to what happens when you hold anything in one position with your muscles contracted continuously.
What happens next is your arch linkage drops and eventually can lock. What I have found is that the arch drops and locks primarily at the second metatarsal cuneiform joint and the third. For those of you who are not doctors that is around the middle of the foot.
People know me as the “anti-shoe” doctor and the “barefoot running” doctor.
Ideally we should be shoeless and constantly moving like our ancestors were.
Click here to read Was My Chronic Pain, Fatigue, Fibromyalgia Cured with a Pair Of Shoes? NO!
So why does a barefoot running doctor recommend shoes in some instances?
That’s because we are supposed to keep moving for optimal use of our spring mechanism. When we keep moving we keep springing.
Some of us might think that healthy movement for the human spring mechanism is in the direction that stimulates development of the spring muscles that spring you forward as in running straight. This would be similar to someone doing the bench press and curls in weightlifting.
We used to see athletes only doing bench press and curls in the gym and we know what happened to those athletes. They got shoulder, back and neck conditions as well as injuries.
Then someone came up with the bright idea that we had to exercise muscles that control the movements of all the joints in all ranges of motion. That way we could develop a more balanced joint motion and strength.
Running training in my opinion is still in the dark ages of development. Many of us still run straight ahead with little to no directional changes. That is, in my opinion, why many of you have conditions related to imbalances of strength in the spring suspension system.
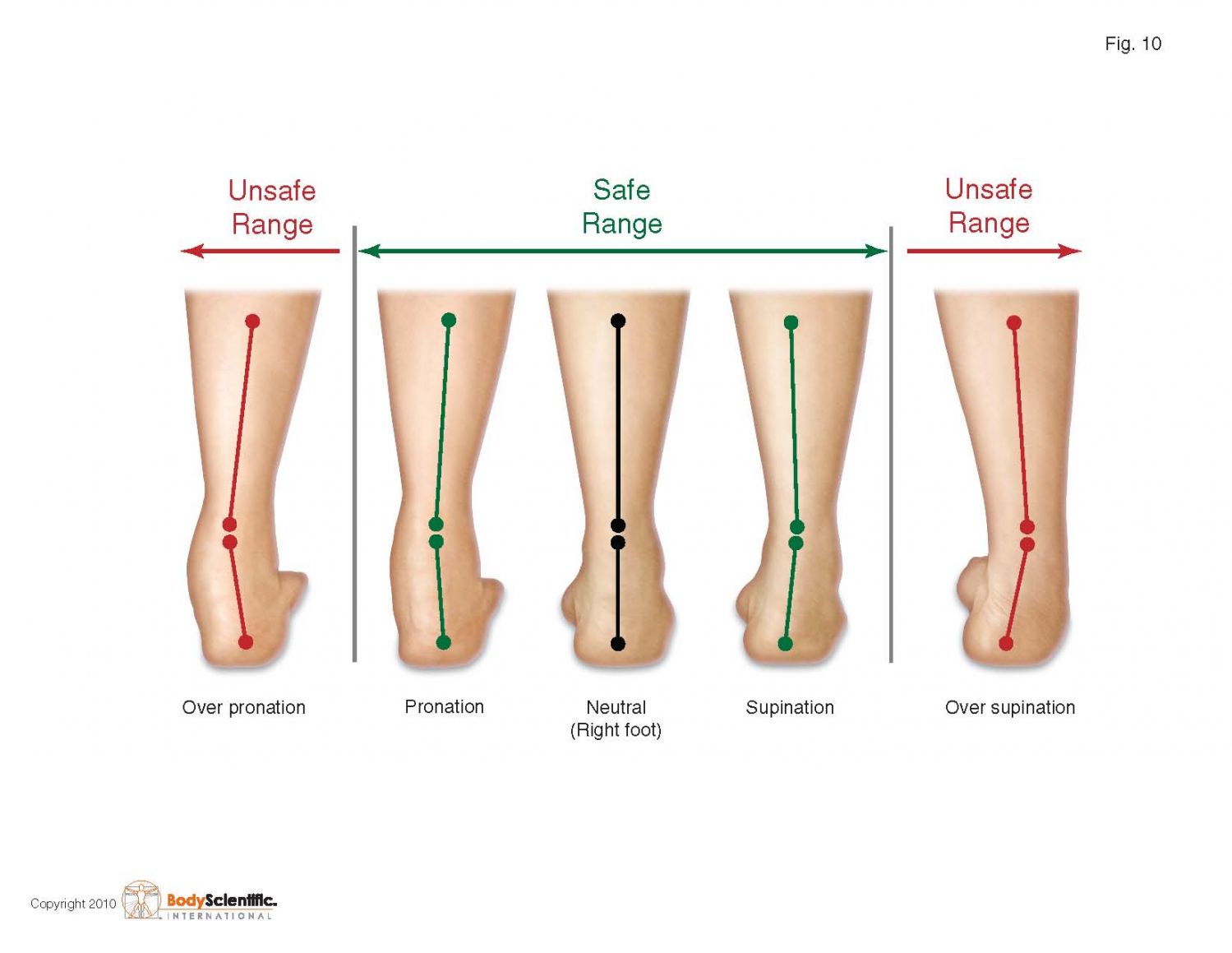
Experts throw the concept of over pronation (over rolling of the foot into the unsafe range inward) and over supination (over rolling of the foot into the unsafe range outward) What is actually being described is the position of the foot at the impact point and through the point when it pushes off.
For those who understand training bone and joint position is controlled by muscle strength.
muscle strength is important to maintain the bones in the position during standing, walking impact forces, running impact forces and endurance strength for many impacts.
If you are running you must run drills in all directions the foot and body moves for a balanced spring mechanism to withstand the impact forces.
This comes directly from the book Supertraining by Siff and Verhkoshansky:
MECHANICAL LOADING OF COLLAGENOUS TISSUE:
(page 41)Since stretching is a particular type of mechanical loading, application of stretching can be more effectively applied if the effects of the loading on collagen are studied carefully. In fact physiological stretch of this possible because collagen and is a viscoelastic material that is, under rapid loading it behaves elastically while under gradual loading it is viscous and can deform plasticity.
(page 42) Since tendons and ligaments are viscoelastic, they also exhibit sensitivity to loading rate, and undergoes stress relaxation, creep and hysteresis. Prolonged and excessive stretching of this type encourages joint mobility at the expense of its stability sold at a joint then has to rely more on its muscles for stability. Despite the widespread opinion that the muscles act as efficient synergistic stabilizers, it should be remembered that the musculature cannot respond quickly enough to protect a joint against injury if large impacts are applied rapidly, particularly Lee if they are torsional since joint stability involves three-dimensional actions over several degrees of freedom, the necessity for appropriately conditioned in all the interacting soft tissues becomes obvious.
Plasticity defined in physics from Wikipedia below:
In physics and materials science plasticity describes the deformation of a material undergoing non-reversible changes of shape in response to applied forces.[1] For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the material itself. In engineering, the transition from elastic behavior to plastic behavior is called yield.
Plastic deformation is observed in most materials including metals, soils, rocks, concrete, foams, bone and skin. However, the physical mechanisms that cause plastic deformation can vary widely. At the crystal scale, plasticity in metals is usually a consequence of dislocations. In most crystalline materials such defects are relatively rare. In brittle materials such as rock, concrete, and bone, plasticity is caused predominantly by slip at microcracks.
For many ductile metals tensile loading applied to a sample will cause it to behave in an elastic manner. Each increment of load is accompanied by a proportional increment in extension, and when the load is removed, the piece returns exactly to its original size. However, once the load exceeds some threshold (the yield strength), the extension increases more rapidly than in the elastic region, and when the load is removed, some amount of the extension remains.
However, elastic deformation is an approximation and its quality depends on the considered time frame and loading speed. If the deformation behavior includes elastic deformation as indicated in the adjacent graph it is also often referred to as elastic-plastic or elasto-plastic deformation.
Perfect plasticity is a property of materials to undergo irreversible deformation without any increase in stresses or loads. Plastic materials with hardening necessitate increasingly higher stresses to result in further plastic deformation. Generally plastic deformation is also dependent on the deformation speed, i.e. usually higher stresses have to be applied to increase the rate of deformation and such materials are said to deform visco-plasticity.
Flow Plasticity theory, uses a set of non-linear, non-integrable equations to describe the set of changes on strain and stress with respect to a previous state and a small increase of deformation.
If the stress exceeds a critical value, as was mentioned above, the material will undergo plastic, or irreversible, deformation. This critical stress can be tensile or compressive. The Tresca and the von Mises criteria are commonly used to determine whether a material has yielded.
DEFORMATION THEORY:
There are several mathematical descriptions of plasticity. One is deformation theory (see e.g. Hookes Law where the stress tensor (of order d in d dimensions) is a function of the strain tensor. Although this description is accurate when a small part of matter is subjected to increasing loading (such as strain loading), this theory cannot account for irreversibility.
Ductile materials can sustain large plastic deformations without fracture. However, even ductile metals will fracture when the strain becomes large enough – this is as a result of work hardening of the material, which causes it to become brittle. Heat treatment such as annealing can restore the ductility of a worked piece, so that shaping can continue.
Science tells us that standing for a long time and even slowly delivered impacts can stress tendons, joints and other tissues to deform their shape weakening the stability and performance. They can be referred to as plastic deformity vs elastic deformity.
In fact sports research found that the shorter the contact time of your foot or bodyweight on the ground the more it improves performance.
Its obvious that standing for a long time is really damaging to our joints!
If the muscles which maintain the foot in the safe range from supination to pronation are not able to maintain them in the safe range then we have to strengthen them.
You would think that athletes would be able to maintain the foot in the safe range during standing for long periods of time.
IN other words if an athlete works all day standing as a teller in a bank they could do it no problem.
If you gave a typical woman’s purse to an athlete and told him to hold it in the 90 degree curl position for 20 minutes he or she would be feeling the strain of the constant contraction burning in the muscles and the strain on the joints as they compressed from the constant pulling and the attachment of the tendons to bones. Pretty soon if it was left long enough they would end up with a condition that had to be treated.
There is no difference with constant contraction related to standing in one position for too long.
Ok, we understand that and I realized long ago this was a problem for me as I stand for long periods of time in one position treating patients. This is especially true when I’m performing one of my pain exorcisms which is body work to release spasms that compress joints from the foot to the head lasting sometimes 2 – 10 hours on one patient.
Tip One:
– Rock and Roll The Feet – What I try to do is rock back and forth into supination and pronation. This keeps your muscles contracting and not stagnating into fatigue. Sometimes I get distracted and forget.
When I forget then the fatigue sets in and my foot starts rolling out of the safe range.
What I have found is that once the spring suspension system muscles fatigue on me my foot will roll either in or out of the safe range either over pronation (85% of the population) or over supination (15% of the population) as a compensation and due to weakness.
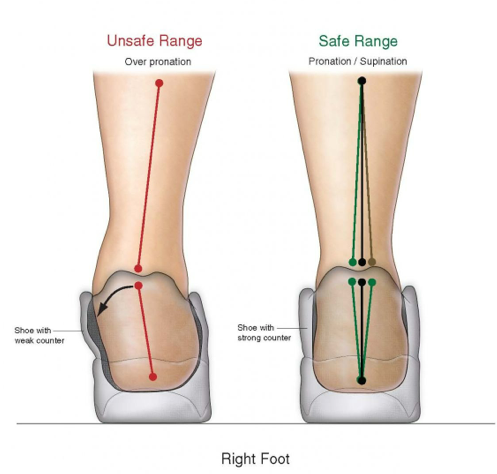
What I found as the best way to balance this negative is to find a shoe that kept my foot in the safe range as long as possible until I could get off my feet and release the muscle tension and fatigue.
Tip Two:
– I wear a shoe with a very strong reinforced counter support.
I have also found some footwear with an extended medial counter support that may extend 2 – 4 inches across the sides of the heel to keep the heel from rolling out of the safe range.
The other important feature I like in my shoes are those with a hard plastic encased inside the leather as a reinforcement.
This is especially important for those who are on their feet for a long time, those of you who see their feet roll out of the safe range or have been told they have over pronation of the feet or over supination of the feet.
Also, many of you who are a little or a lot bigger (you know who you are) and those who have big feet, should seek out the extended medial counter shoe.
It’s interesting that shoe companies design shoes of a size 8 with the same counter support material as a shoe size 14. Dont they realize that a man or woman with a size 14 impacts the ground with more force than a person with a size 8 even if they are an ideal body weight?
This is just poor engineering. If I had my own shoe company I would change that but until then you can use the tips here to do what you can to avoid illness and injury from standing on your feet too long.
Tip Three:
– Release your feet and legs when you get home with the spring release techniques I give you below in tutorial 77 – 89:
Video Tutorial #77 How to Self Adjust Your Toes
Video Tutorial #78 Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Knee Popliteus Muscle
Video Tutorial #79 Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Gluteus Medius Muscle of the Hip
Video Tutorial #80 Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Subtalar Joint Of The Ankle On The Inside
Video Tutorial #81 Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Ankle (Subtalar Joint Outside)
Video Tutorial #82 Deep Tissue Treatment Under The Big Toe And Second Toe
Video Tutorial #83 Deep Tissue Treatment Above The Big Toe And Second Toe
Video Tutorial #84 Scissor Stretching Of The Feet
Video Tutorial #85 Great For Mortons Neuromas And Narrow Heels
Video Tutorial #86 Dr James Stoxen DC Recommends The Best Shoes To Prevent The Foot From Deforming
Video Tutorial #87 Deep Tissue Of The Ankle Mortise
Video Tutorial #88 Stretching Of The Foot While Sitting At Your Chair
Video Tutorial #89 A Stretch To Increase The Flexibility Of The Arch Of Your Foot
Tip Four:
– Walk, Jog or Run Barefoot in zig zag, circle and figure eight directions to release the human spring and strengthen it in a balanced range of motion
Watch this video to see two time Taekwondo National Champion Christian Medina and Dr. Stoxen run barefoot in zig zag patterns.
I also suggest you read Anthony Field’s book, How I My Wiggle Back. He is an entertainer who followed my approach and it helped him change his life. The book has over 200 tips for you in the 100 pages of content that are on the Human Spring Approach.
Like this article? We will send the next one to you.
Register for our updates below:
Disclaimer
All content on teamdoctorsblog.com, including without limitation text, graphics, images, advertisements, videos, and links (“Content”) are for informational purposes only. The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical treatment, advice, or diagnosis. Please remember to always seek the advice of a qualified physician or health professional with any questions you may have regarding any medical concerns. Dr James Stoxen DC and Team Doctors does not recommend or endorse any specific treatments, physicians, products, opinions, research, tests, or other information it mentions. Said Content is also not intended to be a substitute for professional legal or financial advice. Reliance on any information provided by Team Doctors is solely at your own risk.
Contraindications:
There are times when you should refrain from massage or deep tissue massage because it may adversely affect a health condition.
Contraindication is the medical term for these conditions. “Contra” means against, as in contrary, and indications are things that tell you what to do one way or the other. Therefore, contraindications are things that are telling you not to do something.
- Fever: When you have a fever, your body is trying to isolate and expel an invader of some kind. Massage increases overall circulation and could therefore work against your body’s natural defenses.
- Inflammation: Massage can further irritate an area of inflammation, so you should not administer it. Inflamed conditions include anything that ends in itis, such as phlebitis (inflammation of a vein), dermatitis (inflammation of the skin), arthritis(inflammation of the joints), and so on. In the case of localized problems, you can still massage around them, however, avoiding the inflammation itself.
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure means excessive pressure against blood vessel walls. Massage affects the blood vessels, and so people with high blood pressure or a heart condition should receive light, sedating massages, if at all.
- Infectious diseases: Massage is not a good idea for someone coming down with the flu or diphtheria, for example, and to make matters worse, you expose yourself to the virus as well.
- Hernia: Hernias are protrusions of part of an organ (such as the intestines) through a muscular wall. It’s not a good idea to try to push these organs back inside. Surgery works better.
- Osteoporosis: Elderly people with a severe stoop to the shoulders often have this condition, in which bones become porous, brittle, and fragile. Massage may be too intense for this condition.
- Varicose veins: Massage directly over varicose veins can worsen the problem. However, if you apply a very light massage next to the problem, always in a direction toward the heart, it can be very beneficial.
- Broken bones: Stay away from an area of mending bones. A little light massage to the surrounding areas, though, can improve circulation and be quite helpful.
- Skin problems: You should avoid anything that looks like it shouldn’t be there, such as rashes, wounds, bruises, burns, boils, and blisters, for example. Usually these problems are local, so you can still massage in other areas.
- Cancer: Cancer can spread through the lymphatic system, and because massage increases lymphatic circulation, it may potentially spread the disease as well. Simple, caring touch is fine, but massage strokes that stimulate circulation are not.Always check with a doctor first.
- Other conditions and diseases: Diabetes, asthma, and other serious conditions each has its own precautions, seek a doctor’s opinion before administering massage.
- Pregnancy: No deep tissue work. Be aware: danger of triggering a miscarriage by strong myofascial work is greatest during the first 3 months (especially through work around the pelvis, abdomen, adductors, medial legs, or feet)