Over Pronation ICD-9 781.99
What Is Foot Pronation And Foot Supination? Is It Good Or Bad?
Tips For Better Health
Ask the doctor, Dr. James Stoxen DC
You go to your doctor and they say,
“Your feet pronate too much or over pronate.”
Im sure that is what someone said to you which prompted you to google this article.
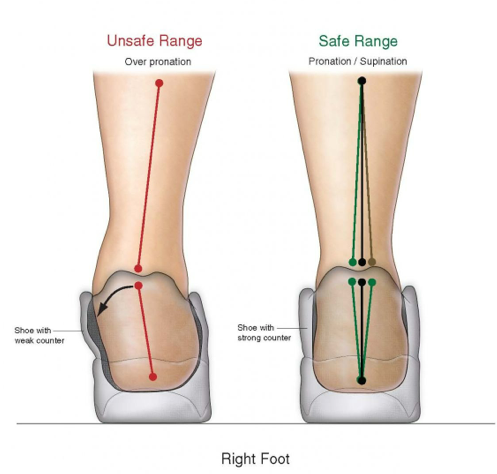
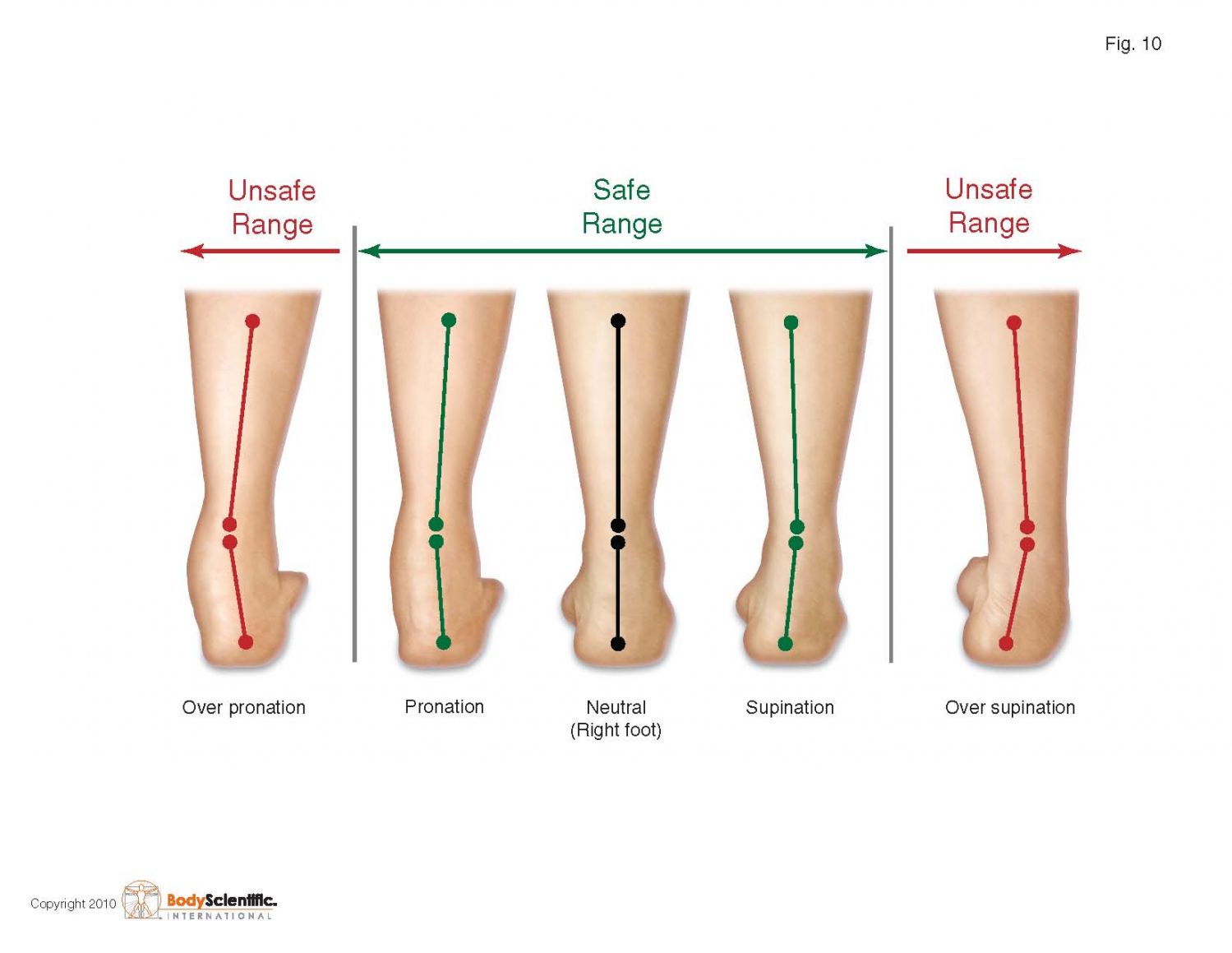
There are many ways to describe over pronation but the way I describe it is when the foot rolls outside a range I call the safe range between rolling from the outside of the foot to the inside of the foot.
This is what many call over pronation, excessive pronation, hyper pronation or sometimes called fallen arches.
Have you been told by your doctor that you have flat feet? Or do your feet supinate too much which is called over supination or excessive supination?
Pronation vs supination, which one is good or bad for you? and Why?
If you look at the biomechanical functions of the foot, during the normal gait cycle (walking cycle) the foot can pronate in many different ways based on rearfoot function (how the heel of the foot reacts) and forefoot function (how the front of the foot or toes react to the landing).
Both pronation and supination are natural, normal motions of the foot.
Pronation is a normal part of the gait cycle (walking/running) which helps to provide shock absorption at the foot. Normal pronation is the movement of the subtalar joint (between the talus and calcaneus) into foot eversion (turning the sole outwards), foot dorsiflexion (pointing the toes upwards) and finally foot abduction (pointing the toes out to the side).
The problem tends to be when someone pronates too much or supinates too much. This places extra stress on the foot and can result in running injuries, walking injuries, serious foot injuries and lower body injuries such as iliotibial band syndrome of the knee, heel spurs, ball of foot pain (metatarsalgia) Achilles tendinitis, plantar fasciitis (heel pain), shin splints, cracking knees (chondromalacia), illiotibial band syndrome, hip pain, lower back pain and muscle weakness.
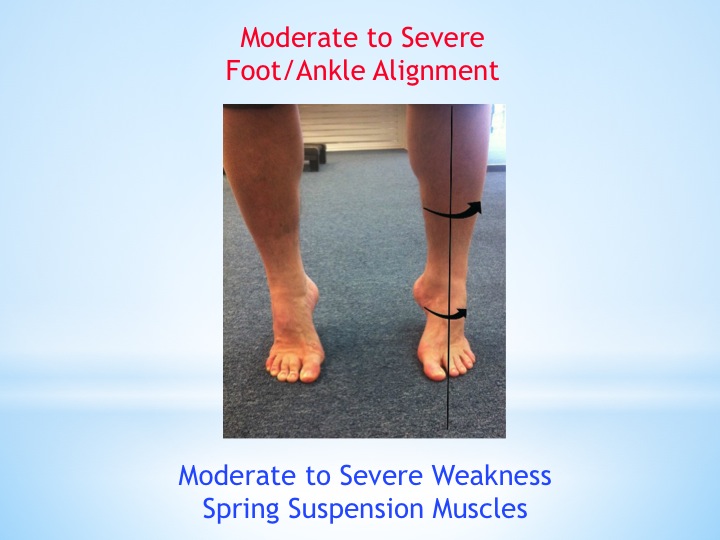
EXCESSIVE PRONATION, Also referred to as overpronation is a biomechanical problem when the foot lands, rolls from the outside to the inside too far outside the safe range.
When it rolls too far outside the “safe range”, most of the person’s body weight is placed on the inner side of the foot while he’s walking, running or performing sports.
Pronation is a normal occurrence in the walking cycle.
The rolling is one of the ways the body safely lands the bodyweight when earths gravity pulls it to the ground. First it rolls the weight across from the outside (supination) to the inside (pronation). Second it loads the weight into the foot with the spring down and spring up of the arch and the spring suspension system muscles.
For more information on how the body absorbs impacts safely and how to improve your ability to absorb these impacts safely read these two posts. They are longer articles with graphics and videos to help you to better understand this so you can help yourself.
When the arch mechanism, specifically its suspension system consisting of the muscles and tendons I call the landing muscles, spring suspension system muscles cannot handle the force of the rolling inward. This is when a person’s arch collapses upon weight bearing.
The rolling of your foot to best absorb the force of impacts from walking or running is part of the normal gait cycle, allowing the foot to absorb shock and adjust to uneven surfaces.
However, too much of this motion (excessive pronation, over-pronation) can cause stress or chronic inflammation on the planter fascia ligament (plantar fasciitis), and lead to numerous other foot and ankle injury related conditions.
The Human Spring Model and Approach I developed has a simple explanation for why we get plantar fasciitis, shin splints and other impact related conditions.
The body has a natural spring mechanism to absorb the forces of the landings. If your natural spring mechanism is weak or locked then it cannot absorb the total force of the impacts from walking and running which means some of the force is absorbed by your plantar fascia, shin bone and muscles and other weight bearing structures like your knees, hips and spine.
Over time, the force of the impact is absorbed into the tissues which can lead to conditions such as Achilles tendinitis, bunions, heel spurs, metatarsalgia, Morton’s neuroma, plantar fasciitis (heel and arch pain), post-tib tendinitis, shin splints, tarsal tunnel syndrome, as well as knee pain (chondromalacia, iliotibial band syndrome), hip pain and lower back discomfort. Related conditions include corns, calluses and hammertoes.
When standing too long, your heels and/or kneecaps may lean or turn inward, and you may abnormally wear out the soles and heels of your shoes very quickly. This is very common in people with flexible, flat feet. Flat feet may be hereditary or caused by obesity or pregnancy. Arches can also fall from trauma (from sports, repeated stress) and wearing shoes that bind the natural spring mechanism for long periods not allowing it to spring during walking. Use it or loose it is the key and if you cannot use it because it is tied up by a shoe it will weaken.
Our feet are the foundation of our body. So poorly aligned feet can have a profound effect on our legs, knees, hips and lower back. A person with pronation of the foot generally walks abnormally, on the inner edge of the foot.
Acquired flat foot syndrome or over pronation are conditions which are related to weakness in these muscles or over working these muscles. These muscles are overworked most commonly when you are standing in one position for a long time with sustained muscle contraction of these suspension system muscles. For more information on this read this post….
Video Tutorial # 159 – Foot Lock! What You Get From Standing Too Long And How To Prevent It
Undiagnosed and untreated, excessive pronation may lead to serious foot injuries and lower body injuries. Among the most common injuries are flat feet, weak arches, bunions, corns, calluses, plantar Facsitus (heel pain), Achilles Tendonitis (tendon pain), frequent ankle sprains, shin splints and knee, hip and back pains.
Are you a pronator of the foot or a supinator of the foot? Do you pronate too much, which is called over pronation or do you supinate too much which is called over supination? What is Supination of the foot? Is foot pronation and supination good or bad?
Both foot pronation and foot supination are natural, normal motions of the foot. Foot pronation occurs as the foot strikes the ground to allow for better shock absorption. The foot rolling inward absorbing the impact is the foot going through a pronation motion. Foot Supination occurs as the foot prepares to toe-off to provide a rigid platform for leverage.
You can do a foot pronation test by looking at the biomechanics of the foot, during a gait cycle analysis, which is a method used to assess the way we walk or run to highlight biomechanical abnormalities.
This causes a chain reaction of damage called a cascade.
If you have over pronation:
It is impossible to get complete healing to maximum medical improvement of an ankle, knee, hip, lower back disc conditions without correcting the weakness in the suspension system or a properly fit extended medial counter support shoe.
for more in helpful information go to Video Tutorial #97 On Your Feet All Day? Fatigued? Achy? Over Pronation? I Recommend Footwear with Extended Medial Counters, click here
The negative cascade is predictable and looks something like this.
- Weakness in the foot spring suspension system muscles leads to excessive over rolling of the foot outside the safe range (over pronation)
- This over rolling leads to abnormal movement patterns in the entire chain of bones above to the head.
- The brain recognizes this abnormal movement but does not know how to fix it. It reacts with muscle spasms that contract to try to prevent the abnormal movement but they cannot. These spasms bring the bones together compressing the entire human spring mechanism. This pattern of spasm is predicted according to how the person compensates for the over pronation and what footwear they have on.
- Simple walking causes stress and strain and with the compressive force from the spams leads to wear and tear of the joints.
- This leads to the release of inflammation.
- Inflammation begins silent or non painful up the predicted pattern of muscle spasm.
- Some of the joints that get more wear and tear, stress and strain start to hurt when the concentration of the inflammation exceeds what the brain can pick up as pain.
- Since the left leg moves an average of 5000 rotations and the right leg moves and average of 5000 rotations together the lower back and spine moves 10000 rotations. This is why the lower back tends to hurt before the feet, ankles, knees and hips. This is more than likely the reason why most doctors are thrown off to the true cause of lower back pain in patients. They don’t see the connection with the over pronation on the side of the back pain.
- Inflammation, if left unchecked is a risk for conditions like depression. For more information read this post and watch the video of my lecture, The Empathy Deficit in the Treatment of Depressed Patients and The Inflammation-Depression Connection Approach, I presented at the 4th Anti-Aging And Regenerative Medicine Conference, Bangkok, Thailand 2012 September 7-9, 2012
- Chronic levels of inflammation is also linked to other diseases of aging such as heart disease, some cancers, Parkonsins, Alzheimers and many others. For more information read this post, Video Tutorial #37 Aches, Pains, Allergies, Fatigue, Brain Fog, Diseases of Aging Have One Common Thread… INFLAMMATION
Also, for you athletes, this misalignment brings about muscular inefficiency, reducing speed and endurance while walking or running.
At first, excessive pronation (hyper-pronation) or over supination may cause fatigue. However problems may get worse, strain on the tendons, muscles and ligaments of the foot and lower leg can cause permanent damage over millions of impacts. They are called plastic deformities. For more information on what elastic deformities (good) vs plastic deformities (bad) are read this post: The Human Spring, A Logical Way to Look At the Way The Body Works?
Conditions which can result are Hallux Abducto Valgus (bunions), having a painful heel (plantar Facsitus), Hallux Rigidus (stiff 1st toe), Anterior compartment syndrome of the lower leg, Metatarsalgia (ball of the foot pain), Shin Splints, Arch Pain, Achilles Tendonitis, Ankle Sprains, Osteochondrosis, Corns & Calluses, Knee Pain, (Illotibial band syndrome of the knee) Flat Feet, Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) and Hammer Toes.
In this article I will explain in detail what is foot pronation and foot supination. As well as ways to prevent over supination of the foot and over pronation of the foot. I will also share exercises to prevent excessive pronation as well as what kind of shoes to look for to prevent foot overpronation.
The body’s weight is absorbed In two very interesting ways:
1. Foot Roll
When the foot first lands, it rolls, distributing the weight across the foot over a time so it is absorbed gradually in a healthy way without causing shock to the skeleton. The foot rolls from supination (the outside) to pronation (the inside). This is called ‘the Foot Roll.’
Stay within the safe range:
In order for the foot to land safely without damaging the body, it must roll within a safe range. That means if the foot starts rolling too far on the outside or rolls too far to the inside, it causes the twisting of the lower leg limb. This twisting force will cause abnormal stress and strain through the muscles, ligaments and tendons of the knee, hip, ankle, lower back, lower spine and up through the head which can cause damage.
The chief characteristic of this arch is its elasticity, due to its height and to the number of small joints between its component parts. Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
When we have a weakness in the core of our body that leads to stress on the spine, we don’t brace the spine and tell the patient that they must be in this brace for the rest of your life, we mobilize the area and prescribe exercises that will keep the area moving in all directions that support the area ranges of motion plus we tell them that they must do these exercises for the rest of their life.
It’s the only thing you know…..
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is the most common cause of acquired flatfoot deformity in adults. The arch is further supported by the plantar aponeurosis, by the small muscles in the sole of the foot, by the tendons of the Tibialis anterior and posterior and Peronæus longus, and by the ligaments of all the articulations involved. Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
The Peronæus longus also everts the sole of the foot, and from the oblique direction of the tendon across the sole of the foot is an important agent in the maintenance of the arch. Henry Gray (1825–1861). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
Primary care physicians often see patients who have foot pain. Although foot disorders may have many diagnostic possibilities, the majority can be explained via the pathologic biomechanics of hyperpronation and the resulting changes in the kinetic chain.
Four common problems often associated with hyperpronation are
- Bunions – Hallux Valgus
- Metatarsalgia – Pain in Ball of Foot
- Foot Pain – Plantar Fasciitis
- Calf Cramps – Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
- Shin Splints – Read this article…
- Cracking Painful Knees – Chondromalacia – Read this article…
- Hip Pain
- Lower Back Pain
Interventions that seek to reduce hyperpronation and strengthen foot muscles are often recommended for treating foot pain.
The muscles that assist in the negative or eccentric loading the force of impacts during walking running or the performance of sports or leisure activities are sometimes forgotten by doctors and trainers.
Why hasn’t my doctor or trainer talked about these muscles? (see above)
What are the muscles of the Pronation Supination Cuff, which I also refer to as the Landing Muscles or the Spring Suspension System Muscles?
We have to begin by learning about the muscles that we need to strengthen.
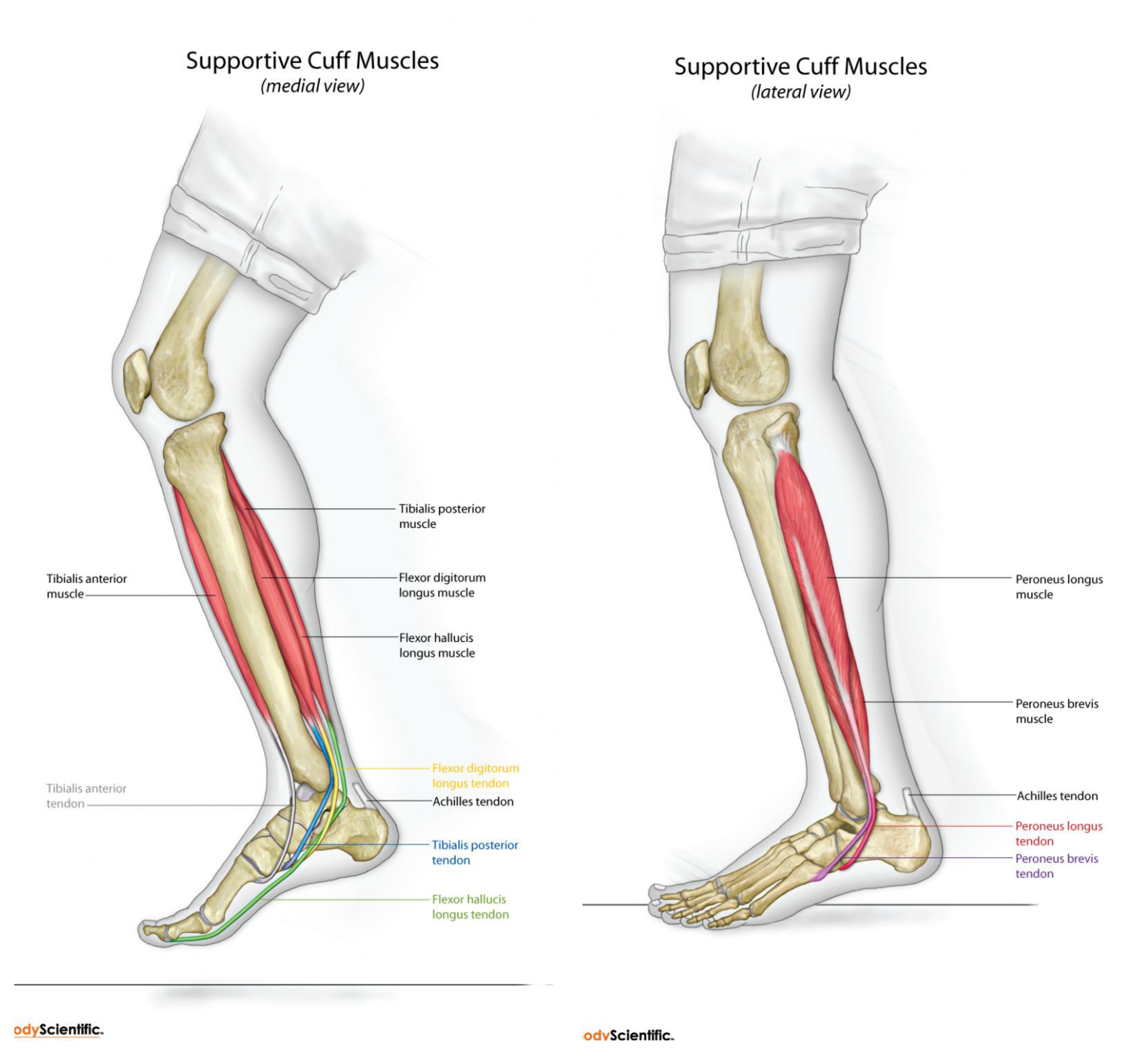
The muscles of the spring suspension system of the foot and ankle consist of the tibialis posterior, tibialis anterior, peroneus longus, and peroneus brevis.
The Tibialis Posterior Muscle (blue tendon)
The tibialis posterior (blue tendon) is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the posterior compartment of the leg.
It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg.
You can also see the tibialis posterior (blue tendon) which attaches at the mid-arch at the first second and third metatarsal cuneiform joints where the spring action happens on impact.
If this joint area is stiff or locked then the tibialis posterior cannot contract maximally against this joint. It’s impossible if the joint is locked. I find this muscle to be the weakest of the cuff.
They even have a syndrome named for it:
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is the most common cause of acquired flat foot deformity in adults. Although this term suggests pathology involving only the posterior tibial tendon, the disorder includes a spectrum of pathologic changes involving associated tendon, ligament, and joint structures of the ankle, hindfoot, and midfoot.
Early recognition and treatment is the key to prevention of the debilitating, long-termconsequences of this disorder. Conservative care is possible in the earliest stages, whereas surgical reconstruction and eventually arthrodeses become necessary in the latter stages. The purpose of this article is to review the symptoms, physical examination, radiological examination, classification, and treatment of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. / Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2000;30:68- 77.
The Peroneus Longus and Brevis
As you can see (pictured above) the peroneus longus (pink tendon) comes from the lateral aspect of the foot cross over to add some support to the first ray.
The Peronæus longus also everts the sole of the foot, and from the oblique direction of the tendon across the sole of the foot is an important agent in the maintenance of the arch.
In human anatomy, the peroneus longus (also known as fibularis longus) is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg, and acts to evert and plantar flex the ankle. The muscle, the longest and most superficial of the three peroneus muscles, is attached proximally to the head of the fibula and its ‘belly’ runs down most of this bone. It becomes a tendon that goes posteriorly around the lateral malleolus of the ankle, then continues under the foot to attach to the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal.
The peroneus brevis muscle (or fibularis brevis) lies under cover of the peroneus longus, and is a shorter and smaller muscle. It is also innervated by the superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve. The muscle acts in plantarflexion and eversion of the foot.
2. Foot Spring
The other way the foot absorbs the body weight is to spring down and spring up. We call this spring load, and spring unload. When the foot lands, it springs down and it stores energy. This spring down creates shock absorption and allows the foot to absorb the body weight over time which prevents shock to the skeleton.
This shock absorption also creates an absorption of energy or potential kinetic energy into the spring. Think of pushing down on the spring of a ballpoint pen. This is called potential energy. When you let go, it snaps backward.
This spring energy is located in a three arch configuration which for all our purposes of simplicity is in the arch itself. The spring energy also comes from the muscles and the tendons that stretch when the foot descends.
You have to have the strength of 1.25 x bodyweight in your suspension system muscles to safely absorb forces from walking speeds, 3x bodyweight to absorb forces from running and everything in-between can be estimated.
So if you look in the mirror while standing and you observe an excessive over pronation at 50% of bodyweight – half your weight on each foot that your spring suspension system can absorb 2-3 times your bodyweight for thousands of impacts during jogging or running. I don’t care if you have an artificial spring (cushioned shoe) or not. The forces of impacts are not that much different with a cushion.
The only footwear design that may temporarily help you is the counter support mechanism. Read this article for more information on the shoe design I recommend when you HAVE TO wear shoes for training.
Was My Chronic Pain, Fatigue, Fibromyalgia Cured with a Pair Of Shoes? NO!
Video Tutorial #86 Dr James Stoxen DC Recommends The Best Shoes To Prevent The Foot From Deforming
If you have over pronation while you are standing you have no business running. Your suspension system cannot handle these forces. Would you attempt to lift 200 pounds when your body can lift only 150? Of course not. The difference is the effects of the stress and strain with each impact accumulate so for many of you it confuses you where the pain is coming from.
You MUST train barefoot to completely develop your NATURAL spring mechanism for the long term.
Read this article on why I run barefoot to see why I am adamant about this!
Training the Muscles of the Pronation Supination Cuff/The Spring Suspension System Muscles/The Landing Muscles:
There are two training methods that must be employed to develop these muscle groups:
- The first way is training the suspension system muscles as a lever mechanism, with resistance exercises.
- The second phase of exercises involve training the body as a spring mechanism with impact exercises.
First of all these exercises must be done barefoot or in socks. Any binding device such as a shoe and even those minimalist shoes will inhibit the movements of adduction, abduction, inversion, eversion, pronation and supination.
When doctors and scientists claim that footwear doesn’t inhibit the movement, they are defending footwear. They quickly ask for research that claims that it inhibits movement. Certainly, anyone can do a study that determines what range of motion a healthy human being can get without footwear or barefoot. As well as a study with certain types of footwear that are wrapped around the foot and tied around the foot.
The focus of movements which they base these studies are usually plantar flexion and dorsi flexion. They do not focus on the movements that are vital to the strengthening of the suspension systems such as inversion, eversion, adduction and abduction.
In order to get the maximum range of motion (inversion, eversion, adduction and abduction), you must train barefoot!
Phase I – release all the spasms and locking of the joints that are interfering with the natural stress and strain free loading of the force of the landings.
I have all the deep tissue self massage treatments that you can do on the floor of your living room here.
Look at the videos below where I show you how to release the human spring with my deep tissue release tips:
Be sure to start on Video Tutorial # 78 and go through Video Tutorial #89:
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Self-Help, Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Knee Popliteus Muscle
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Self-Help, Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Gluteus Medius Muscle of the Hip. This can be helpful for hip conditions.
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates How To Self-Help Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Ankle (Subtalar Joint Inside). This can be helpful for heel pain.
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates How To Self-Help Deep Tissue Treatment Of The Ankle (Subtalar Joint Outside) This can be helpful for heel pain.
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Self-Help Deep Tissue Treatment Under The Big Toe And Second Toe
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Self-Help Deep Tissue Treatment Above The Big Toe And Second Toe
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Scissor Stretching Of The Feet
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Stretching. This can be helpful for Mortons Neuromas
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Recommends The Best Shoes To Prevent The Foot From Deforming
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Self-Help Deep Tissue Of The Ankle Mortise.
This can be helpful for ankle conditions
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates Stretching Of The Foot While Sitting At Your Chair
Watch above as Dr James Stoxen DC Demonstrates A Stretch To Increase The Flexibility Of The Arch Of Your Foot
Phase II- Training the suspension system muscles as a lever mechanism, with resistance exercises.
One might think that’s it’s impossible to train the feet just like we do our upper body because we can’t grab a weight with our foot like we can with our hands.
It did take some ingenuity to be able to develop a way of strengthening the foot and ankle muscles like we do muscles of our arms etc.
Currently, to my knowledge there are no machines specifically designed for this purpose.
Resistance Band Training – Of course you can attach rubber bands to the feet and exercise them that way. (I have never found this to be so effective, as the band tension changes the further we stretch it).
I prefer to use the cuff with the low pulley mechanism to do these exercises.
I have some other really effective ways to train this area listed at the end of this article that you may like.
I developed a novel way to strap the weights to the foot, ankle and other body parts with cuffs made from Velcro or with belt buckle types of connections to the foot.
The number one priority is to exercise the muscles which support and strengthen the human spring first.
You will find from reading this post that even if we are exercising according to the current guidelines set by accredited fitness organizations and professionals that these programs are incomplete.
I have researched the top 20 books published on fitness training and found that not one of them adequately addresses the spring suspension system or the spring support system of the remaining 7 floors.
Remember, You must do these exercises barefoot!
Also over reliance on ergogenic devices such as lifting belts, hand grips bandages for the joints special shoe inserts wedges for squatting, elastic training shirts can modify the neuromuscular system to such an extent that efficient or safe training without them becomes difficult. Professor Yuri Verhkoshansky
Book: Supertraining, Dr Mel Siff & Professor Yuri Verhkoshansky
I really can’t understand how people think that they can put a binding device on their foot and tie it tight and then think they’re going to be able to get full range of motion in the foot during motions outside of just running straight ahead. It’s ridiculous to think that it’s possible because it absolutely is not possible to get full development of these muscles with a shoe on.
For those of you who are required to wear workout shoes at your fitness center, I suggest that you bring this blog post or send this post to the manager of your fitness center. Then ask them if they can have an area specifically for training with bare feet or with socks.
This builds floors 1 – 3, however many train with their shoes on and the exercises are not as effective as the ones we teach in the Human Spring Approach. We don’t see this as part of the core routine yet. That is something that definitely needs to change.
I am about to explain to you the spring suspension system training routine that will fill the gap to the exercises that are missing from the training routine for running and bodybuilding. This is the area that is missing from your fitness routine as you are only training the muscles from floor three through seven.
Smart people train the spring suspension system muscles if they’re looking to have long-term fitness results rather than short-term and to prevent a high risk of physical breakdown of the spring suspension system.
You are doing the right thing for your future.
Cuff With Rope and Weight Method:
You can get a cuff from from any fitness store that will wrap around your foot and has a hook for attaching low pulleys, resistance bands or just a rope.
You can attach the cuff around your foot and then tie a rope to the couch and at the other end of the rope tie a free weight, a gallon of milk in a plastic container full of sand under one fourth of the way full, one half full or full of sand, or anything that provides various resistance.
What you do next is either drag this object across the ground either in the sand, in the grass, on your carpet, on the street, or through the snow by isolating the pulley through your foot and ankle in the motions of inversion, eversion, abduction, adduction, plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, and combined movements of pronation and supination.
examples of this kind of exercise are below:
Video Tutorial #105 Foot Eversion Exercise, click here to view
Video Tutorial #106 Foot Inversion Exercise, click here to view
Cuff With Resistance Bands Method
There are many companies that will sell you resistance bands of variable resistance. These are popular with hard-core trainers who know the value of training these body parts that are not considered the Hollywood beauty muscles but more for function.
What I like about these bands is that they’re portable so you can put them in your suitcase or your bag and bring them with you anywhere in the world. What I don’t like about them is that the resistance increases as the band is stretched further rather than a constant resistance of dragging weight or lifting a weight.
I still think this method is a fantastic approach to develop the muscles of the feet and worth every minute of time in this method for long-term goals.
You train the exact same way as other resistance exercises doing either sets of 15, 12, 10, eight, six, four’s, threes or triples depending on if you want to build strength or power or both.
You train this area 3 days a week for fitness or 2 days a week with a light day and a heavy day for power and speed.
Video Tutorial #148 Bosu Ball Foot Training, click here
Video Tutorial #76 Bosu Ball Lateral Step, click here
Video Tutorial #177 Side Lunge With Cable, click here
Video Tutorial #105 Foot Eversion Exercise, click here
Video Tutorial #106 Foot Inversion Exercise, click here
Video Tutorial #107 Ankle Exercise Training, click here
Video Tutorial # 108 Cable Hip Adduction And Foot Inversion, click here
Video Tutorial #109 Hip Adduction Exercise by Miguel Macho Hernandez, click here
Video Tutorial #109 Hip Abduction Exercise by Miguel Macho Hernandez, click here
Video Tutorial #111 Rectus Abdominal Cable Crunch Pull Downs, click here
Video Tutorial #112 Abdominal Oblique Exercise, click here
Video Tutorial #176 Half Foam Roll Exercises, click here
The muscles of the foot, called the spring suspension muscles, must be strong in order to prevent over rolling or supination or pronation to maintain the foot in a safe range. Many of you may not have strong enough spring suspension system muscles to be able to overcome over supination or over pronation. As I stated above, this can cause damage.
Phase III – Do spring training exercises which are multidirectional drills and or plyometrics.
We don’t only walk or run straight ahead but we also change our direction. We MUST do exercises such as side shuffles or Zig Zag runs as well as other movements besides walking straight ahead. That is because these muscles are stimulated during zig zag, side to side and circular running.
Watch Video Tutorial #133 Circle Walk, Jog, Run, click here
Read Video Tutorial #179, 45 Degree Zig-Zag Hop, Jump Or Run, click here
The foot and ankle are three-dimensional objects which requires them to have balance and strength in all ranges of motion for the structure to work according to way we were designed.
Many Doctors and scientists think the body moves only in four directions claim that the body uses a stiff lever system to push off.
This is simply not possible when the mechanism is functioning the way it was intended. Doctors admit that during impact, the foot rolls from supination to pronation as and at the same time, it loads energy from the top to the bottom of the arch mechanism.
This combination of movements; rolling in and loading, makes it impossible for the foot to go into a stiff lever position at any given time. This is because it is a dynamic structure that is moving with what we call it elastic deformity, storing energy within the deformation of the foot shape as well as deformation of the tendons making them longer then snapping back to their original length. Dr James Stoxen DC
When impact involves a changing of length of the tendon as it stretches to load the arch then snaps back to unload the arch we have to say that this is not a lever system as is normally described in current literature.
As the foot, ankle and its tendons returns back to their exact original shape they are releasing FREE energy by recycling energy within the spring mechanism.
Do you need a shoe when performing impact drills?
Then doctors who claim the body as a lever system and defend footwear is binding as non-consequential to the health of the human foot quickly contradict themselves by saying that shoes are required to support the foot during impacts.
If something is claimed to be supporting the structures of the foot then it has to apply a force against it to maintain it in the position of support.
So claiming that a shoe cannot be inhibiting motion and at the same time claiming that it inhibits motion by supporting it is a contradictory statement.
Individually, each person who reads this has different fears or concerns regarding doing impact drills without support. Gymnasts certainly impact the ground in multiple directions when doing tumbling exercises.
In my opinion, if we can do impact drills without supports interfering with normal adaptation then we should do these multi directional impact drills without external supports.
Do I do zig-zag runs, circle runs, shuffle runs, ricochet and cariocca drills barefoot? Of course I do!
Anyone that tells you this has not thought this out carefully both theoretically and considering simple common sense.
Can you get hurt doing these drills barefoot?
Of course you can:
- if you have a preload compressive force in the spring mechanism prohibiting the maximum force of impact to load safely into the spring
- If your running form and technique does not provide for a safe loading the forced of the landing into the spring
- If you do not run in a safe environment.
I train my spring suspension system 100% of the time when running barefoot by running in multiple angles.
I do my barefoot running as a training exercise by running the entire 5 to 6 miles in zigzag patterns of approximately 2 to 3 feet on either side of the imaginary straight line, highway divider line or line in the sidewalk or street.
Normal force = perpendicular to the ground and the spring
Forces must land with the center of gravity perpendicular to the spring for maximum protection. If the part is symmetrical then distribution of forces over the human spring center of gravity are more efficient.
Pronator Supinator Cuff AKA Arch Sling, Arch Spring Cuff; The Spring Cuff Or The Spring Suspension System
When we are training with impact drills we are primarily strengthening the tendons and connective tissue structures that increase true spring strength.
For example it has been found that much of the most selective in running is associated with tensioning of the tendons, which thereby store energy for successful cycles of movement (Cavagna 1977).
This tensioning or rewinding of the tendon fibers burned largely isometric muscle contractions is achieved with very little change in the length of the muscle fibers themselves.
The fact that the forces involved are derived mainly from isometric contractions means a decreased energy expenditure because isometric and attractions are mode dynamically are considerably less expensive than dynamic contractions. Supertraining Yuri Verkhoshansky Mel C. Siff
I call these muscles the pronator supinator cuff, another word for them could be the arch spring cuff; the spring cuff or the arch spring suspension system like a car. These muscles perform movements that you may not be aware of called foot inversion, foot eversion, foot abduction and foot adduction, the combined movements of foot pronation and foot supination.
These muscles are not well known by trainers and doctors because they are somewhat complicated, but I will make it easy on you. These muscles are like interlocking fingers of your hands that keep the foot safe from rolling too far into supination and pronation. They keep the foot in the safe range.
The most important muscles in this area are called the tibialis posterior, tibialis anterior, and the peroneal muscles. These muscles are more important to understand than the quads, glutes, hamstrings or abbs because they maintain the human spring and without health in the human spring or the foundation of your body your entire body will collapse.
Inflammation Patterns / External Forces
To summarize, everyone is guilty of foot supination and foot pronation. If not, we’d have a difficult time walking or running. The problem tends to be when someone pronates too much or supinates too much . Too much pronation is called overpronation. This occurs when the arch collapses either at too much of an angle or it stays collapsed too long through the gait cycle. If the foot overpronates during the gait cycle analysis, there is a distinctive inward collapse of the arch. It’s hard to see with the untrained, naked eye at full speed, but on video it’s very apparent. That is why I recommend doing a gait analysis.
Develop your spring suspension system muscles and spring suspension system with impacts. It is best for your long term health and an anti-aging lifestyle!
“Champions will do what others don’t want or can’t do and that’s why they are champions!”
Dr James Stoxen
This video excerpt was taken from the lecture Presentation: 
Abnormal Biomechanics And The Aging Process
At The 1st Anti-Aging International Symposium And Exposition
Tokyo, Japan
June 16-18, 2006